The Complete Guide to Protein Digestion: From Fork to Muscle
The Complete Guide to Protein Digestion
We’ve all heard the hype about protein: it’s the key to building muscle, boosting energy, and supporting overall health. But here’s the catch—eating a protein-packed meal doesn’t automatically mean your body can use it. Digesting protein is a complex, multi-step process that requires a well-coordinated team of enzymes, hormones, and other players. If your system isn’t ready, you might not be getting the full benefits of that chicken breast or protein shake. In this blog, we’ll break down the science of protein digestion, explain the concept of bioavailability, highlight the challenges, and share practical solutions to help you make the most of your protein intake.
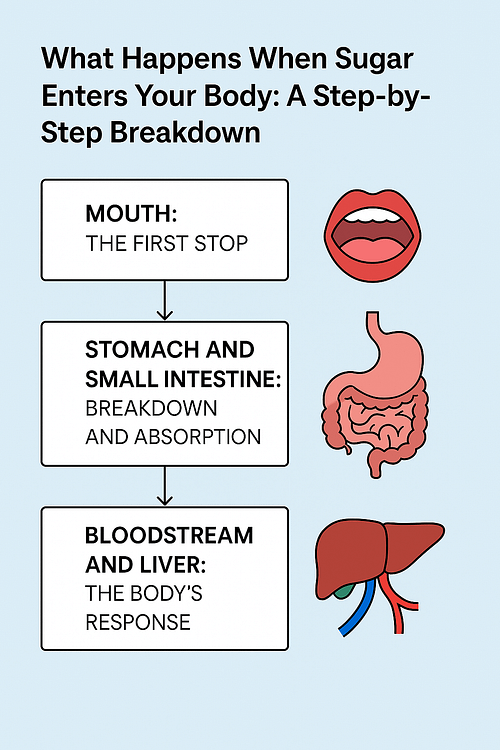
The Protein Digestion Highway: A Step-by-Step Journey


Stage 1: The Mouth – Setting the Foundation
Digestion begins before you even swallow. Your teeth mechanically break protein into smaller pieces, dramatically increasing surface area for enzymatic action. While saliva doesn’t contain protein-specific enzymes, thorough chewing is crucial—it can improve protein digestibility by up to 25%.
The science: Each chew breaks food into smaller particles, allowing stomach acid and enzymes better access to protein structures. Studies show people who chew each bite 30-40 times extract significantly more amino acids from their meals.
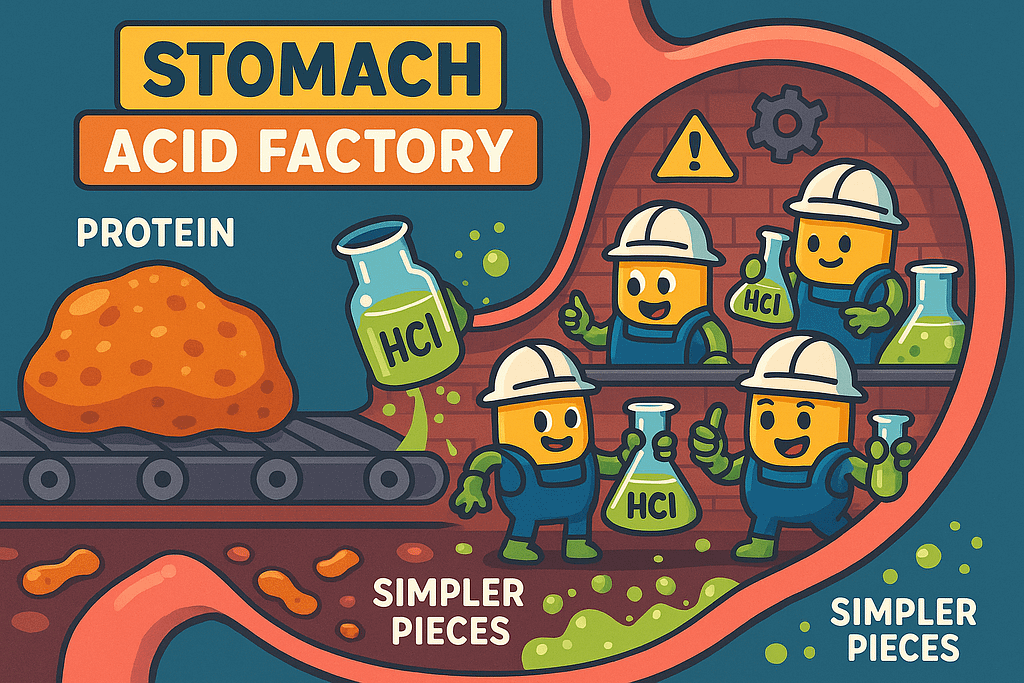
Stage 2: The Stomach – Chemical Breakdown Central
Your stomach is essentially a highly acidic protein processing plant. When protein arrives, several critical processes begin simultaneously:
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) Production: Your stomach produces acid with a pH of 1.5-2.0—nearly as acidic as battery acid. This extreme acidity serves multiple purposes:
- Unfolds complex protein structures (denaturation)
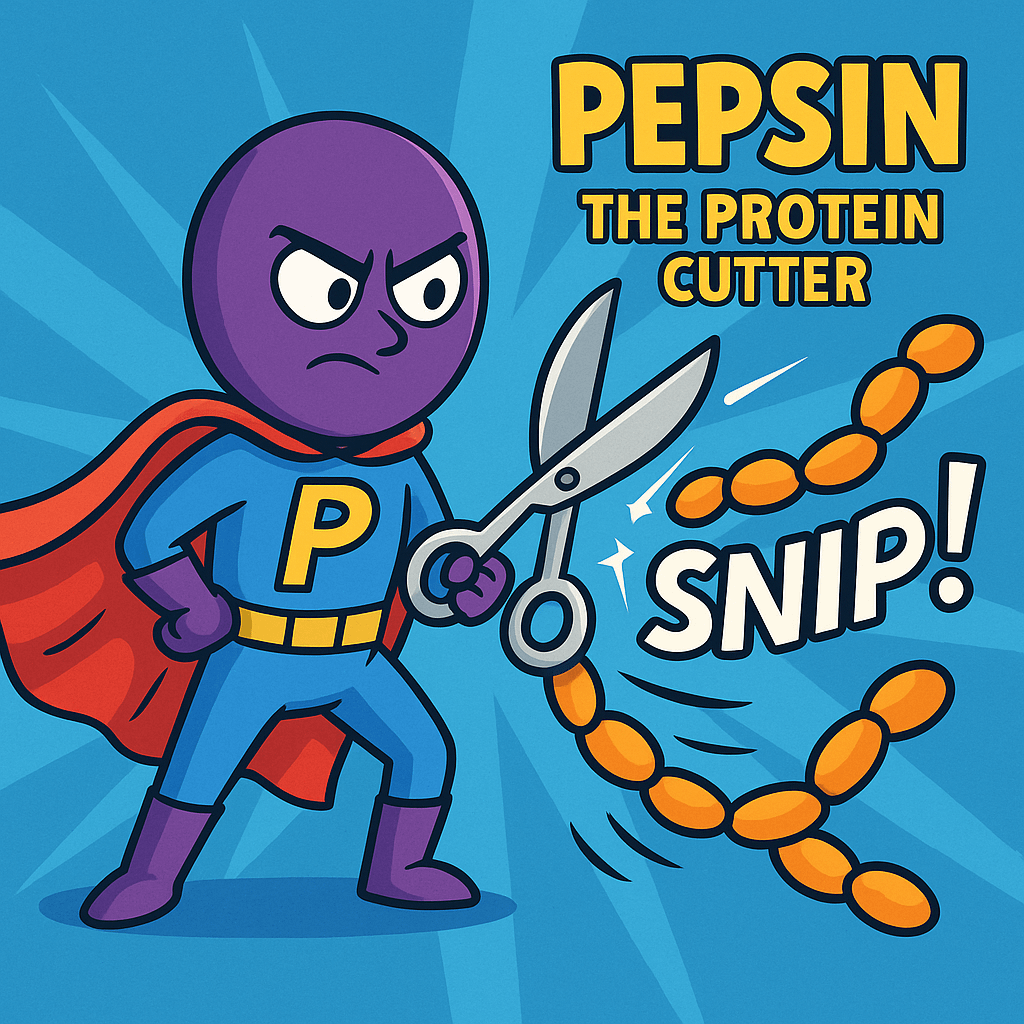
- Activates pepsinogen into pepsin, your first protein-digesting enzyme
- Kills harmful bacteria that might interfere with digestion
- Signals the pancreas to prepare its enzyme arsenal
Pepsin Action: Once activated, pepsin begins cleaving proteins at specific amino acid sequences, particularly around aromatic amino acids like tryptophan and phenylalanine. This creates smaller protein fragments called polypeptides.
Critical insight: Low stomach acid (hypochlorhydria) affects up to 30% of adults over 65 and can reduce protein digestibility by 40-60%. Common causes include stress, certain medications (especially proton pump inhibitors), and H. pylori infections.
Stage 3: The Small Intestine – The Enzymatic Powerhouse
The small intestine is where protein digestion reaches its peak efficiency. As the acidic stomach contents (called chyme) enter the duodenum, a cascade of events occurs:
Pancreatic Enzyme Release: The pancreas releases bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid and deploys three major proteases:
- Trypsin: Cuts proteins after basic amino acids (lysine, arginine)
- Chymotrypsin: Targets aromatic amino acids (tryptophan, tyrosine, phenylalanine)
- Carboxypeptidase: Removes amino acids from protein chain ends
Brush Border Enzymes: The intestinal lining contains specialized enzymes that complete the breakdown:
- Aminopeptidases: Remove amino acids from the amino end of peptides
- Dipeptidases: Break dipeptides into individual amino acids
- Tripeptidases: Split tripeptides into smaller units
Absorption Mechanism: Amino acids are absorbed through specific transporters in the intestinal wall. Different amino acids use different transport systems, which is why amino acid timing and combinations matter for optimal absorption.
Stage 4: Cellular Delivery and Utilization
Once absorbed, amino acids enter the hepatic portal circulation, traveling directly to the liver for processing. The liver acts as a quality control center, regulating amino acid release into systemic circulation based on the body’s needs.
Hormonal Signaling: Protein digestion triggers several important hormones:
- Cholecystokinin (CCK): Signals satiety and stimulates enzyme production
- Insulin: Facilitates amino acid uptake into muscle cells
- IGF-1: Promotes muscle protein synthesis when adequate amino acids are available
The Enzyme Army: Your Protein Digestion Workforce


Proteases are highly specialized enzymes that function like molecular scissors, each designed to cut specific amino acid bonds. Understanding these enzymes helps explain why protein digestion can be challenging:
Pepsin (Stomach):
- Optimal pH: 1.5-2.0
- Targets: Aromatic amino acids
- Function: Initial protein breakdown
- Challenge: Requires very acidic environment
Pancreatic Proteases (Small Intestine):
- Optimal pH: 8.0-8.5
- Require: Adequate pancreatic function
- Challenge: Sensitive to inflammation and disease
Brush Border Enzymes (Intestinal Lining):
- Function: Final breakdown steps
- Challenge: Damaged by gut inflammation, food sensitivities, or infections
Protein Bioavailability: The Quality Equation


Not all proteins are created equal. Bioavailability measures how efficiently your body can digest, absorb, and utilize a protein source. This depends on several factors:
Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS)
High-Quality Proteins (PDCAAS 1.0):
- Eggs: Complete amino acid profile, easily digestible
- Whey protein: Rapid absorption, high leucine content
- Fish: Complete proteins with beneficial omega-3s
- Lean meats: Complete but slower-digesting than whey
Moderate-Quality Proteins (PDCAAS 0.7-0.9):
- Soy protein: Complete but contains antinutrients
- Quinoa: Complete plant protein but lower total protein content
- Hemp protein: Good amino acid profile but high fiber
Lower-Quality Proteins (PDCAAS 0.4-0.7):
- Rice protein: Low in lysine
- Pea protein: Low in methionine
- Wheat protein: Low in lysine, contains gluten
Factors Affecting Bioavailability
Processing Methods: Heat treatment can improve digestibility by denaturing proteins but excessive heat damages amino acids, particularly lysine. Optimal cooking temperatures range from 60-80°C for most proteins.
Antinutrients: Plant proteins often contain compounds that inhibit digestion:
- Phytates: Bind minerals and proteins, reducing absorption
- Lectins: Can damage intestinal lining
- Trypsin inhibitors: Block protein-digesting enzymes
Food Combinations: Strategic pairing can enhance protein utilization:
- Rice + beans = complete amino acid profile
- Vitamin C + plant proteins = improved iron absorption
- Healthy fats + protein = slower digestion, sustained amino acid release
Common Protein Digestion Challenges


Age-Related Decline
Protein digestion efficiency decreases with age due to:
- Reduced stomach acid production (30-40% decrease after age 60)
- Decreased enzyme production
- Slower gastric emptying
- Reduced muscle mass affecting amino acid utilization
Solution: Older adults may need 1.2-1.6g protein per kg body weight (vs. 0.8g for younger adults) and should focus on high-quality, easily digestible proteins.
Digestive Disorders
Low Stomach Acid (Hypochlorhydria):
- Symptoms: Bloating, undigested food in stool, B12 deficiency
- Causes: Stress, certain medications, autoimmune conditions
- Impact: 40-60% reduction in protein digestibility
Pancreatic Insufficiency:
- Symptoms: Fatty stools, weight loss, nutrient deficiencies
- Causes: Chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, diabetes
- Impact: Severe protein malabsorption
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO):
- Symptoms: Gas, bloating, diarrhea after protein meals
- Mechanism: Bacteria compete for amino acids, produce toxic byproducts
- Impact: Reduced amino acid absorption, increased inflammation
Dietary Transition Challenges
When increasing protein intake, many people experience:
- Bloating and gas (bacterial fermentation of undigested protein)
- Constipation (inadequate fiber and water intake)
- Kidney strain myths (actually unfounded in healthy individuals)
- Digestive fatigue (system overwhelmed by sudden increase)
Evidence-Based Optimization Strategies







Enhance Digestive Capacity
Support Stomach Acid Production:
- Consume protein with acidic foods (lemon juice, apple cider vinegar)
- Avoid large amounts of water during meals (dilutes acid)
- Manage stress through meditation, adequate sleep
- Consider betaine HCl supplements if deficient (under medical supervision)
Boost Enzyme Production:
- Include natural enzyme sources: pineapple (bromelain), papaya (papain), ginger (zingibain)
- Eat slowly and chew thoroughly
- Avoid excessive antacid use
- Consider digestive enzyme supplements for persistent issues
Optimize Protein Timing and Distribution
Protein Distribution Research: Studies show that consuming 20-30g of high-quality protein every 3-4 hours maximizes muscle protein synthesis better than consuming the same total amount in fewer, larger doses.
Pre and Post-Workout Timing:
- Pre-workout: 15-20g protein 1-2 hours before training
- Post-workout: 20-30g protein within 30-60 minutes after training
- Choose fast-digesting proteins (whey) post-workout, slower proteins (casein) before bed
Support Gut Health
Microbiome Optimization:
- Include prebiotic fibers (garlic, onions, asparagus)
- Consume fermented foods (yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut)
- Avoid unnecessary antibiotics
- Manage stress and get adequate sleep
Intestinal Lining Health:
- Include glutamine-rich foods (bone broth, cabbage)
- Consume omega-3 fatty acids to reduce inflammation
- Avoid excessive NSAIDs and alcohol
- Consider zinc and vitamin D optimization
Strategic Food Combining
Enhance Plant Protein Quality:
- Combine complementary proteins within 24 hours
- Add small amounts of animal protein to plant-based meals
- Soak, sprout, or ferment plant proteins to reduce antinutrients
Optimize Absorption Environment:
- Include vitamin C with plant proteins (enhances iron absorption)
- Add healthy fats for fat-soluble vitamin absorption
- Space calcium supplements away from protein meals (can compete for absorption)
Advanced Considerations
Individual Variation
Genetic polymorphisms affect protein digestion:
- Lactase persistence: Determines dairy protein tolerance
- AMY1 gene variants: Affect enzyme production capacity
- COMT gene: Influences response to certain amino acids
Practical application: Pay attention to your individual response to different protein sources and adjust accordingly.
Cooking and Preparation Methods
Optimal Cooking Techniques:
- Steam or poach: Preserves amino acid integrity
- Slow cooking: Breaks down tough protein structures without excessive heat
- Marinating: Acidic marinades pre-digest proteins
- Avoid: Charring, deep frying, or excessive processing
Plant Protein Enhancement:
- Soaking: Reduces antinutrients by 50-80%
- Sprouting: Increases amino acid availability
- Fermentation: Improves digestibility and adds beneficial bacteria
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Persistent Bloating After Protein Meals
Immediate strategies:
- Reduce portion size and eat more frequently
- Try different protein sources to identify sensitivities
- Ensure adequate hydration
- Include digestive enzymes with meals
Long-term solutions:
- Address underlying gut health issues
- Gradually increase protein intake over 2-4 weeks
- Work with a healthcare provider to rule out digestive disorders
Poor Recovery Despite Adequate Protein Intake
Assessment checklist:
- Total daily protein intake (aim for 1.6-2.2g/kg for active individuals)
- Protein distribution throughout the day
- Digestive health status
- Sleep quality and stress levels
- Hydration status
Choosing Supplements Wisely
When supplements may help:
- Digestive enzyme deficiency
- Restricted dietary protein intake
- High training volume requiring convenient protein sources
- Specific health conditions affecting digestion
Red flags to avoid:
- Unrealistic claims about protein requirements
- Proprietary blends hiding actual protein content
- Excessive additives or artificial ingredients
- Lack of third-party testing for purity
The Bottom Line: Patience and Personalization

Optimizing protein digestion is a gradual process that requires patience and individual adjustment. Your digestive system can adapt and improve its protein-processing capacity, but this takes time—typically 2-6 weeks of consistent practices.
Key takeaways:
- Quality matters: Focus on high-bioavailability proteins and proper preparation
- Quantity distribution: Spread protein intake throughout the day for optimal utilization
- Support systems: Maintain healthy digestion through acid production, enzyme function, and gut health
- Individual optimization: Pay attention to your body’s responses and adjust accordingly
- Professional guidance: Consult healthcare providers for persistent digestive issues
Remember, the goal isn’t just to eat protein—it’s to transform that protein into the building blocks your body needs for strength, recovery, and optimal health. By understanding and optimizing your protein digestion, you’re investing in your body’s fundamental ability to repair, rebuild, and thrive.
Master your digestion, master your results.
The Complete Guide to Protein Digestion: From Fork to Muscle Read More »